Jump to: Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | Step 4 | Step 5 | Why not just reference the jar file in the Project Libraries?
A Java based application utilizing a Microsoft Server is an unusual configuration. As such, sometimes drivers have big faults and bar you from using this configuration. This post is an attempt to show how to setup a connection from a Java Web Application to an MS SQL Server. It is not a catch all installation and it might not be applicable to you
Installation Scenario:
In this scenario we are running an MS SQL Server as a database backbone for our Java Web Application. The Java Web Application itself will be run in Apache Netbeans IDE and with of course with Tomcat Apache as our Web Server.
*Keep this scenario in mind as there are parts of this tutorial that might not be applicable to you.
Part 1: Before the driver installation
Of course MS Server and Apache Server should be already be installed and running.
If MS Server isn’t installed follow standard installation process. Download the installer here.
The Apache Server should be installable through Netbeans. If it needs to be installed manually follow standard installation process. Download installer here.
*Note: MS Server by default runs in the 1433 port by default. Make sure no other server / program running in that port (use “netstat -a -b” in cmd for windows). To check what the target port for the MS Server, it’s a good idea to learn SQL Server Configuration Manager.
Part 2: Download the JDBC Driver
Go to this link and download the .zip file for the 8.4 version: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/connect/jdbc/release-notes-for-the-jdbc-driver?view=sql-server-ver15#84
Open the zip file, our interests are these 2 files:
- sqljdbc_8.4\enu\mssql-jdbc-8.4.1.jre14.jar

- sqljdbc_8.4\enu\auth\x64\mssql-jdbc_auth-8.4.1.x64.dll

*Note: We are using the 8.4 version in this tutorial as that’s the one that works. Make sure to test other versions of the driver for compatibility. Also make sure the jar file is compatible with the jre version you are running as the driver jre compatibility is denoted by the .jre14 in our case.
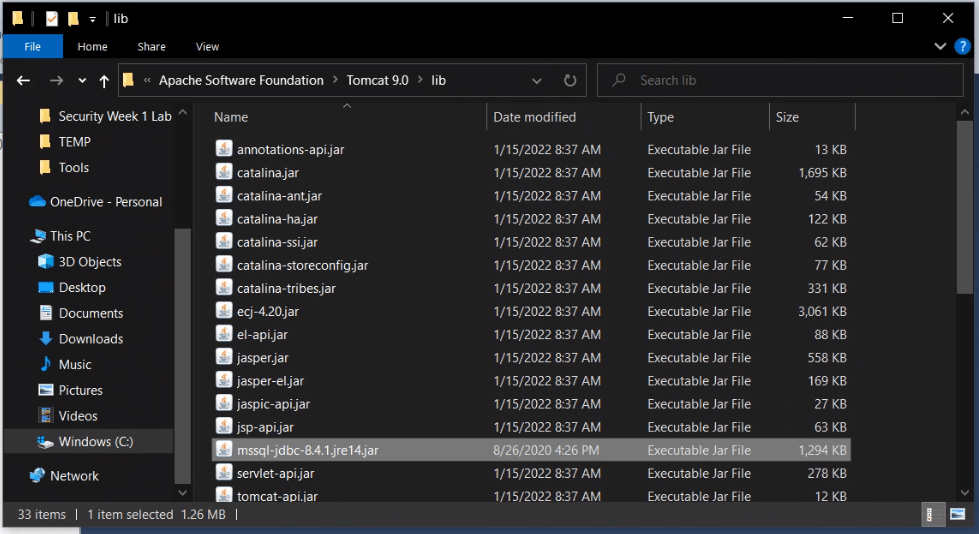
Part 3: Place the driver files in the Apache installation.
Copy the specified files to the Apache installation folder as follows:
Note: Apache’s default install directory is “C:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\”
Part 4: Setting up Java connection
Use the following code to create a connection to the MS Server Database.
// ESTABLISHING CONNECTION
Class.forName("com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver");
Connection conn=null;
// Change DBNAME based on your created database name
String DBNAME = "[DBname]";
// Change localhost: to correct port number if necessary
String connectionString="jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433;databasename="+DBNAME+";"
+ "integratedSecurity=true;"
+ "encrypt=true;"
+ "trustServerCertificate=true;";
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionString);
Use the Connection variable to run scripts, as well as retrieve data from the database.
Part 5: Testing the database connection
First we need to create data to retrieve from the database. Create a database, table and data for testing. In this case I created them using MS SQL Server Management Studio as follows:

In the java application, use this code to attempt a connection to the MS Server.
Connection conn=null;
String DBNAME = "TEST";
try {
// ESTABLISHING CONNECTION
Class.forName("com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver");
// Change "databasename" if you named your database differently
// Change localhost: to correct port number if necessary
String connectionString="jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433;databasename="+DBNAME+";"
+ "integratedSecurity=true;"
+ "encrypt=true;"
+ "trustServerCertificate=true;";
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionString);
// TRYING TO RETRIEVE DATA FROM DATABASE
if(conn!=null)
{
// Basic Select Statement
String query = "SELECT * "
+ "FROM "+DBNAME+".dbo.TESTTable";
PreparedStatement st = conn.prepareStatement(query);
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getString("TESTrow"));
}
st.close();
conn.close();
}
}
catch(Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
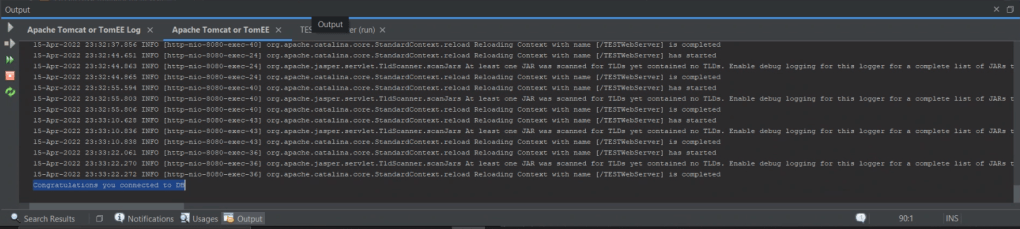
Running the java program should get the data:
Why not just reference the jar file in the Project Libraries?
If you have worked with Java Database drivers before you’d know that usually we include .jar libraries in the Project Library itself so the Java Project can use that .jar library.
In this case, it is important to know that utilizing the MS jdbc Drivers are prone to cause “Unsatisfied link error” exception. With this implementation, the connection is more flawless and causes no exceptions mentioned.